
CSD-KOMP Strategy details
- CSD-KOMP gene targeting constructs are made in two stages.
- Stage one - “intermediate construct”
This multi purpose vector made at CHORI consists of two homology arms, eukaryotic selection marker and LoxP site around critical exon. It allows an exchange of selection marker for variety of custom made trapping cassettes via gateway sites incorporated into intermediate vector. Gateway sites flanking homology arms permit addition of mammalian negative selection markers.
Intermediate construct
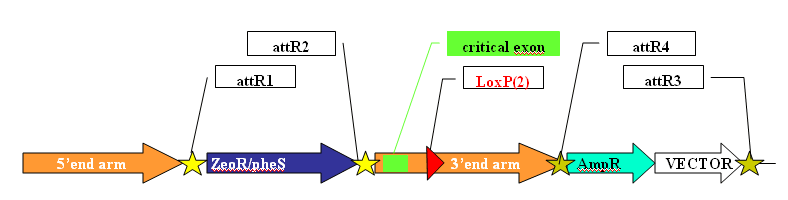
ZeoR/pheS – recombineering cassette flanked by gateway attR1-R2 sites is used as an exchange module with trapping cassettes (betaGal/neo or other ) in gateway L/R reaction. There are 3 exchange modules for each translation frame unless additional IRES provided in front of the marker(s). Zeocin serves as a positive selection marker during homologous recombination in e.coli. Gateway R1-R2/L1-L2 reaction is assisted by pheS negative selection on no-triptone selective media (YEG-Cl)
AmpR-Vector – modular gap repair vector flanked by attR3-R4 sites used in GW_R3-R4/L3-L4 -exchange reaction with pL3/L4/DTA_Kan/Cm_ccdB vector.- Stage two – “final construct” – ready for ES transformation product, includes tested trapping cassette and negative selection marker. Allows conditional with or no reporter KO.
We provide protocols for gateway modifications and a choice of trapping cassettes:- promoterless targeting trapping cassettes – relies on inactivation of genes expressed in ES cells ~50% efficient, increase fraction of correct targets.
- >SA/IRES/lacZ/pA/promoter/neo/polyA – promoter driven trapping cassette provides Neo(G-418) resistance, can be used with all genes.
All custom modifications of trapping cassettes require presence of gateway sites in correct orientation.
Final construct
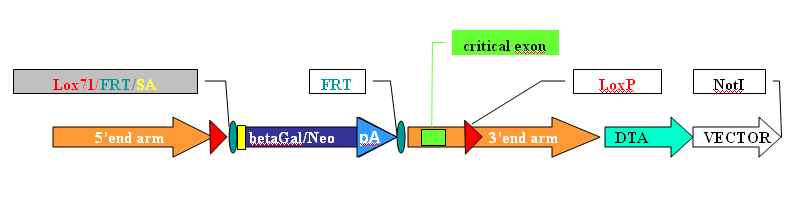 5’-end arm ~ 3-5Kb long, usually doesn’t contain gene promoterbetaGal/neo/polyA – promoter less trapping cassette, located in intron after start of transcription, contains splice acceptor site (SA). In-frame betaGal and neo fusion expression is driven by targeted gene promoter, flanked by FRT sites. Trapping cassette must contain mammalian selection marker, 5’end LoxP, 2 flanking FRT sites and efficient polyA “trapping” sequence to terminate transcription.critical exon(s) – essential for gene functionality, deletion disrupts gene function 2 ways: removing functional domain and creating a frame shift in gene expressionLox71 – taccgttcgtatagcatacattatacgaagttatLoxP – ataacttcgtatagcatacattatacgaagttatLox71 - LoxP genomic distance is ~1Kb, flank a critical exon, work as a pair for conditional cre mediated in vivo deletion of critical exon in mouseFRT - gaagttcctattccgaagttcctattctctagaaagtataggaacttctwo FRT sites used for flp mediated in vivo removal of betaGal/neo-LoxP cassette in ES cells.3’-end arm ~ 3-5Kb longDTA - diphtheria toxin fragment A - PGK promoter driven mammalian negativeselection marker, replaces more conventional TK negative selection, requires FIAU or gancyclovirin.Vector – remaining portion of the vector after linearization with AsiSI, protects DTA from nucleases after electroporation into ES cells
5’-end arm ~ 3-5Kb long, usually doesn’t contain gene promoterbetaGal/neo/polyA – promoter less trapping cassette, located in intron after start of transcription, contains splice acceptor site (SA). In-frame betaGal and neo fusion expression is driven by targeted gene promoter, flanked by FRT sites. Trapping cassette must contain mammalian selection marker, 5’end LoxP, 2 flanking FRT sites and efficient polyA “trapping” sequence to terminate transcription.critical exon(s) – essential for gene functionality, deletion disrupts gene function 2 ways: removing functional domain and creating a frame shift in gene expressionLox71 – taccgttcgtatagcatacattatacgaagttatLoxP – ataacttcgtatagcatacattatacgaagttatLox71 - LoxP genomic distance is ~1Kb, flank a critical exon, work as a pair for conditional cre mediated in vivo deletion of critical exon in mouseFRT - gaagttcctattccgaagttcctattctctagaaagtataggaacttctwo FRT sites used for flp mediated in vivo removal of betaGal/neo-LoxP cassette in ES cells.3’-end arm ~ 3-5Kb longDTA - diphtheria toxin fragment A - PGK promoter driven mammalian negativeselection marker, replaces more conventional TK negative selection, requires FIAU or gancyclovirin.Vector – remaining portion of the vector after linearization with AsiSI, protects DTA from nucleases after electroporation into ES cells - Stage one - “intermediate construct”