| Vector
pBACe3.6 Information/Map |
 |

In the course of our initial work
with PAC libraries and PAC vectors, we obtained feedback from
several sequencing centers who considered the costs of sequencing
PAC versus BAC clones. A disadvantage was the size of
the PAC vector (16 kb left in recombinants) as compared to
the size of the BAC vector (7 to 8 kb, depending on the vector
variant). For the use of BACs versus PACs with inserts
in the range of 100-150 kb, this means that a larger fraction
of the clones in shotgun sequence libraries (M13 or pUC) represents
the PAC/BAC vector sequence. This results in a few percent
increase in the cost per base pair of sequence reads.
We have, therefore,improved
the BAC vector (Shizuya H. et. al. 1992, Proc. Natl. Acad.
Sci. USA 89:8794-8797) to include some of the retrofitting
options included in our pPAC4 vector We also included the
sacBII gene for use as a positive-selection marker to favor
recombinant clones over non-insert background colonies. The
sacBII gene from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens was derived from
Nat Sternberg's P1 vector (Pierce et al. 1992, Proc. Natl.
Acad. Sci. USA 89:2056-2060). The toxicity of the sacBII gene
is a result of the conversion of fructose (derived from sacharose)
into polyfructose (levan), which is toxic in E.coli.
The cloning vector and recombinant clones do NOT
express the sacBII gene and hence are sucrose-resistant. Undesirable
clones derived from the deleted cloning vector (without the
"green" stuffer fragment) are sucrose-sensitive
and ,hence, do not form colonies on sucrose-containing media.
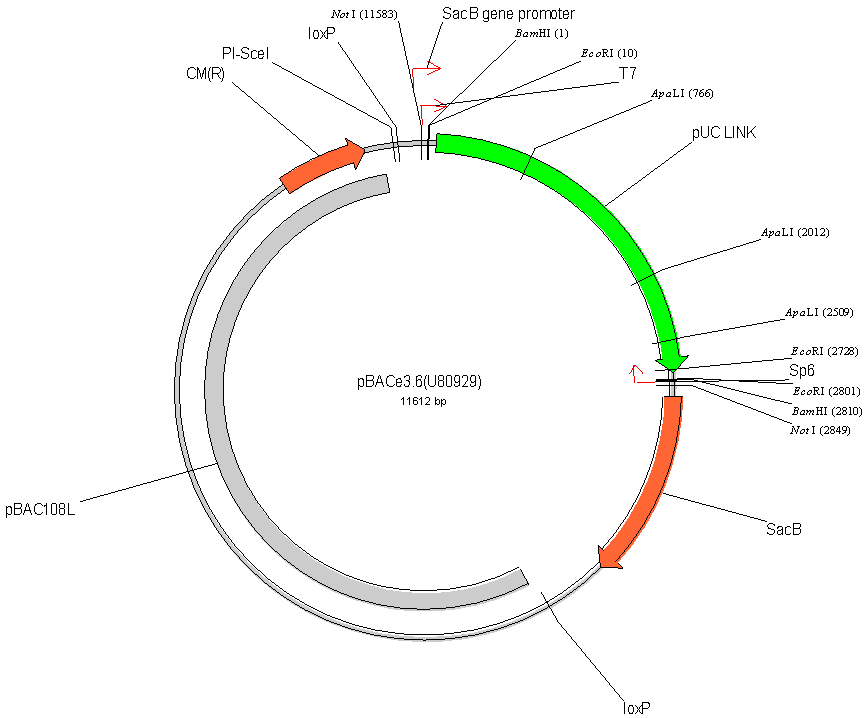
The new vector has
been named pBACe3.6. Specifically, we maintained the
wildtype loxP site, added an additional mutant loxP511 site,
a site for the intron encoded nuclease PI-SceI and the Tn7att
site.
The presence of
this pUC plasmid serves dual functions: high copy number of
the vector for preparing large quantities and appropriate
disruption of the sacBII gene to increase viability of the
vector containing strain. In addition to the BamHI site,
5 additional sites can be used for preparing BAC libraries:
SacI, SacII, MluI, EcoRI, and AvaIII. The EcoRI site
is particularly important in view of the use of this site
in the RARE cleavage procedure, thus opening the possibility
for selective cloning of similar fragments from different
DNA donors.
Reference:
Frengen, E. et al. (1999) A Modular, Positive Selection Bacterial
Artificial Chromosome Vector with Multiple Cloning Sites.
Genomics 58: 250-253. Reprints availiable upon request.
pBACe3.6 clones
have chloramphenicol antibiotic resistance. Clones should
be grown in LB containing 12.5 ug chloramphenicol/ml.
Contact BACPAC Resources ( [email protected]
) for further information regarding current availability
or ordering.
|

